- Kontakt
-
stefan.bente[at]th-koeln.de
+49 2261 8196 6367
Discord Server
Prof. Bente Personal Zoom
- Adresse
-
Steinmüllerallee 4
51643 Gummersbach
Gebäude LC4
Raum 1708 (Wegbeschreibung)
- Sprechstunde nach Vereinbarung
- Terminanfrage: calendly.com Wenn Sie dieses Tool nicht nutzen wollen, schicken Sie eine Mail und ich weise Ihnen einen Termin zu.
Übung »Use Cases«
In dieser Übung gehen wir die Aspekte der Use-Case-Erstellung durch.
Worum geht es?
In dieser Übung entwickeln Sie aus einem Anforderungstext Use Cases, indem Sie die Use-Case-Grenzen festlegen und mittels Kriterien testen, ob die Use Cases die richtige Größe haben. Dann erstellen Sie das Use-Case-Diagramm, und anschließend füllen Sie noch ein detailliertes Szenarien-Template aus.
In der Übung gehen wir ganz ähnlich vor wie auch im entsprechenden Praktikums-Meilenstein.
Anforderungstext
Sie sollen ein Softwaresystem für “EV-Experts.com” erstellen. Nachfolgend finden Sie den Anforderungstext.
(1) EV-Experts.com sells and installs charging stations für EVs (electric vehicles). (2) A customer (who
wants to have a charging station for his EV in his house) fills in a contact form with his name, EV brand
and type, and some house details. (3) The system stores the data, and displays it to a sales person.
(4) The sales person then calls the customer by phone and clarifies what the customer wants.
(5) The sales person then uses a configurator tool to offer a charging station. (6) A charging station
has a price, internal cost, and some details. (7) The sales person emails this to the customer.
(8) If the price is too high for the customer, he/she will walk away and look elsewhere for a charging
station. (9) If the customer accepts the price, the sales person asks an engineer for help.
(10) The engineer immediately opens the planning module (which is a part of the software system
to be implemented) in order to plan the charging station details, and to determine the cost;
this takes ca. 10 minutes. (11) The sales person opens the planning module and enters the customer
name. (12) The system retrieves charging station details and cost, and displays it to the sales person.
(13) The sales person checks if the original price still covers the cost. (14) If yes, the sales
person hands the customer over to the engineer, and the charging station is ready to be built.
(15) If the original price was too low, the sales person adapts the price for the charging station
in his configurator and emails it again to the customer. (16) If the customer doesn't accept
this higher price, he/she walks away. (17) If the customer accepts, the sales person now hands
the customer over to the engineer, and charging station is ready to be built. (18) Usually one
to two months later, the engineer installs the charging station in the customer's house, in coordination
with the customer. (19) If the customer wants to bulk order a lot of charging stations at once, he/she
can call the sales person directly, and they agree how to proceed. (20) In that case, one engineer
is assigned to work fulltime directly with the customer.
1) Festlegung der Use-Case-Grenzen
1.1) Textanalyse für Use-Case-Grenzen
Machen Sie eine Textanalyse wie im Video gezeigt, um die Use-Case-Grenzen zu bestimmen. Kopierend Sie den Text in ein eigenes Dokument, und streichen Sie die Use-Case-Grenzen an. Diskutieren Sie mit Ihren Kollegen über die Lösung! Hinweis: Wir gehen davon aus, dass der Kunde in Satz 8 und Satz 16 sofort reagiert.
Tragen Sie anschließend die Grenzen in diese Tabelle ein:
| Use Case Name | beginnt bei Satz |
|---|---|
| … | … |
Lösung

Das ergibt dann folgende Tabelle:
| Use Case Name | beginnt bei Satz |
|---|---|
| Order charging station | 2 |
| Install charging station | 18 |
| Bulk order many charging stations | 19 |
1.2) Tests der Grenzen
Wenden Sie den User-Happiness- und den Coffeebreak-Test an. Begründen Sie Ihre Entscheidung kurz.
Lösung
- Order charging station
- User Happiness:
- Auftrag für CS ist abgeschlossen - Kunde ist zufrieden.
- Geht es auch kleiner? Könnte man z.B. nach Satz 9 schneiden, wo der Engineer die Konfiguration macht?
- Antwort: Eher nein - der Auftrag ist nicht abgeschlossen, der Preis steht nicht fest, und es dauert auch nur 10 min.
- Coffee break:
- Das Ganze müsste an einem Vormittag durchgehen - also passt es noch grob auf den Coffee Break Test.
- Geht es auch größer? Könnte man die Installation in Satz 18 noch mitnehmen?
- Antwort: Nein - das passiert viel später (1-2 mon).
- User Happiness:
- Die anderen UC sind nicht ausreichend detailliert beschrieben - hier sind die Grenzen recht klar, sie würden sich bei mehr Details aber vielleicht noch aufteilen.
2) Use-Case-Diagramm
Zeichnen Sie das Use-Case-Diagramm.
Lösung
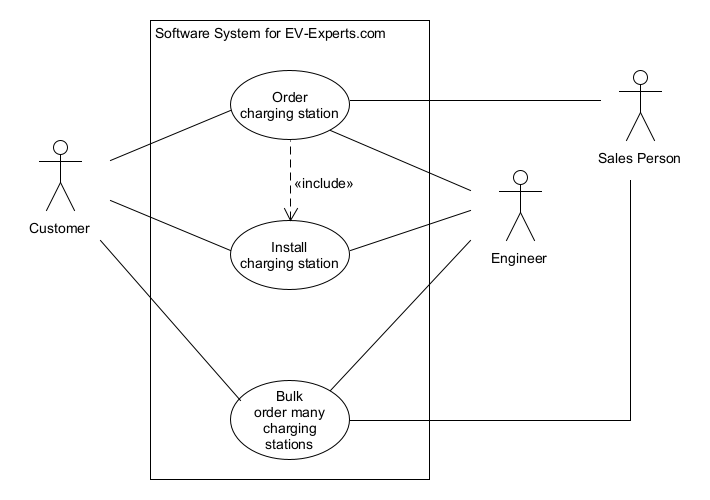
3) Textuelles Use-Case-Szenario
Erstellen Sie in den nachfolgenden Teilaufgaben das textuelle Use-Case-Szenario für den am ausführlichsten beschriebenen Use Case.
3.1) Streichen Sie irrelevante Sätze
Streichen Sie alle Sätze, die für den betrachteten Use Case nicht relevant (kein Aktivitätsschritt) sind.
Lösung

3.2) Markieren Sie die Verben, um die Aktivitäten zu finden
Markieren Sie alle Verben, die eine Aktivität darstellen, und damit dann in dem Szenario auftauchen müssen.
Lösung

3.3) Use-Case-Header
Füllen Sie folgende Tabelle für den Use-Case-Header aus.
| Feld | Wert |
|---|---|
| Name | … |
| Auslösender Aktor | … |
| Weitere Aktoren | … |
| Auslöser | … |
| Vorbedingung | … |
| Nachbedingung | … |
Lösung
| Feld | Wert |
|---|---|
| Name | Order charging station |
| Auslösender Aktor | Customer |
| Weitere Aktoren | Sales person, engineer |
| Auslöser | Customer wants to have a charging station for his EV in his house |
| Vorbedingung | - |
| Nachbedingung | Charging station is now ready to be built |
3.4) Hauptszenario
Erstellen Sie für den Use Case das Hauptszenario. Tragen Sie es in die nachfolgende Tabelle ein.
| Benutzer | System | Externes System |
|---|---|---|
| … | … | … |
| … | … | … |
Lösung
| Benutzer | System | Externes System |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Customer fills in a contact form on EV-Experts.com with his name, EV brand and type, and some house details. | ||
| 2. The system stores the data. | ||
| 3. The system displays it to a sales person. | ||
| 4. The sales person calls the customer by phone. | ||
| 5. The sales person clarifies what the customer wants. | ||
| 6. The sales person then uses a configurator tool to offer a charging station with some details, internal costs, and a price | ||
| 7. The sales person emails details and price to the customer. | ||
| 8. The customer accepts the price. | ||
| 9. The sales person asks an engineer for help. | ||
| 10. The engineer immediately opens the planning module in order to plan the charging station details, and to determine the cost. | ||
| 11. The sales person opens the planning module and enters the customer name. | ||
| 12. The system retrieves charging station details and cost. | ||
| 13. The system displays this to the sales person. | ||
| 14. Sales persons checks if the original price still covers the costs (which it does). | ||
| 15. The sales person hands the customer over to the engineer. |
3.5) Alternativszenario
Erstellen Sie für den Use Case das Alternativszenario, falls es eines gibt.
- Wenn ja, dann tragen Sie es in die nachfolgende Tabelle ein.
- Wenn nein, dann begründen Sie kurz, warum es keins gibt.
| Benutzer | System | Externes System |
|---|---|---|
| … | … | … |
Lösung
| Benutzer | System | Externes System |
|---|---|---|
| 14a1. The sales persons checks the planning tool, if the original price still covers the costs, but the price is too low. | ||
| 14a2. The sales person adapts the price for the charging station in his configurator. | ||
| 14a3. The sales person emails it again to the customer. | ||
| 14a4. The customer accepts the higher price. |
3.6) Ausnahmeszenario
Erstellen Sie für den Use Case das Ausnahmeszenario, falls es eines gibt.
- Wenn ja, dann tragen Sie es in die nachfolgende Tabelle ein.
- Wenn nein, dann begründen Sie kurz, warum es keins gibt.
| Benutzer | System | Externes System |
|---|---|---|
| … | … | … |
| … | … | … |
Lösung
| Benutzer | System | Externes System |
|---|---|---|
| 8b. The customer doesn’t accept the price | ||
| NB: Offer not accepted, charging station not ready to be built, customer walks away | ||
| 14c1. The sales persons checks the planning tool, if the original price still covers the costs, but the price is too low. | ||
| 14c2. The sales person adapts the price for the charging station in his configurator | ||
| 14c3. The sales person emails it again to the customer | ||
| 14c4. The customer doesn’t accept the higher price | ||
| NB: Offer not accepted, charging station not ready to be built, customer walks away |



